Magnification Prior- A Self-Supervised Method for Learning Representations on Breast Cancer Histopathological Images
CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision 2023
Read Paper @ CVF Read Paper + Supplimentary Material Source Code @ Github Watch Video @ Youtube Check Poster
Data scarcity in medical vision is a well-known challenge, especially in histopathology. The problem intensifies when images are captured at different magnifications, as each magnification reveals different details. With limited labeled data and inconsistent image scales, training models becomes even harder.
By using domain-specific insights, this work turns the weakness of varying magnifications into a strength. Instead of standard augmentations used in typical models, we replace them with magnification variations, creating a domain-aware self-supervised learning method.
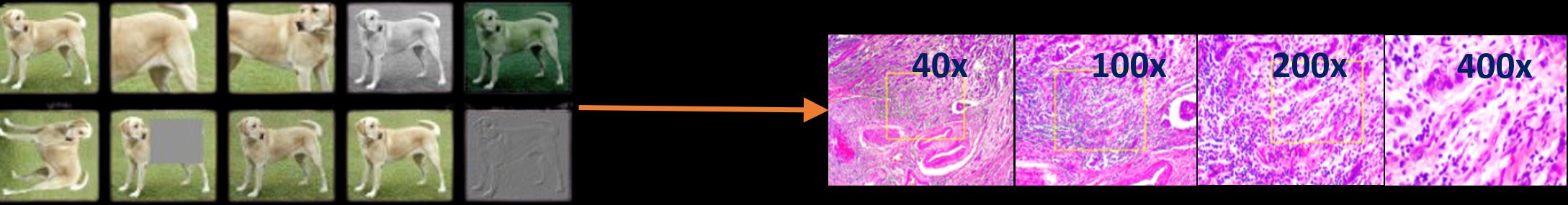
Introducing Magnification Prior Contrastive Similarity (MPCS)—a method that leverages these magnification differences. Rather than relying on conventional augmentations, MPCS uses magnifications to teach the model how to learn from these variations. This leads to robust, self-supervised representations that are perfectly suited for the complex nature of histopathology. The method comes in three variants—Fixed Pair, Ordered Pair, and Random Pair— each using a unique magnification sampling strategy to explore the flexibility and performance of method.
MPCS sets a new benchmark, beating state-of-the-art methods across three histopathology datasets—BACH, Breast Cancer Cell, and BreakHis. These results highlight the method’s resilience and adaptability, proving its dominance in diverse medical imaging challenges.
The ablation study shows how each MPCS variant—Random Pair, Ordered Pair, and Fixed Pair—handles varying magnifications and human priors, with Ordered Pair standing out for its balance of flexibility and accuracy. The t-SNE visualizations confirm its strength, showing clear and distinct clustering of malignant and benign samples across magnifications.
This domain-aware, self-supervised approach reshapes how we tackle the challenges of histopathology, turning magnification variability into a key strength for robust representation learning. To dive deeper, check out the full paper, watch the video on YouTube, and explore the research poster for more insights into the method’s impact.
Read Paper @ CVF Read Paper + Supplimentary Material Source Code @ Github Watch Video @ Youtube Check Poster
Prakash Chandra Chhipa, Richa Upadhyay, Gustav Grund Pihlgren, Rajkumar Saini, Seiichi Uchida, Marcus Liwicki; Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2023, pp. 2717-2727