Depth Contrast - Self-supervised Pretraining on 3DPM Images for Mining Material Classification
European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops 2022
Read Paper @ arxiv Read Paper @ Springer Source Code @ Github Check poster
Challenges in mining material classification extend beyond the scarcity of labeled data. The nature of data itself poses a significant hurdle due to its diverse characteristics captured by specialized sensors. Traditional computer vision models often struggle to handle these differences, highlighting the need for a domain-aware self-supervised learning approach.
To address these challenges, we focus on using domain-specific signals inherent in the data. Specifically, the depth information of materials captured by the 3DPM sensor serves as a valuable signal that can be exploited for self-supervised representation learning. This insight allows us to go beyond conventional image-based methods and leverage the unique properties of mining materials to improve classification performance.
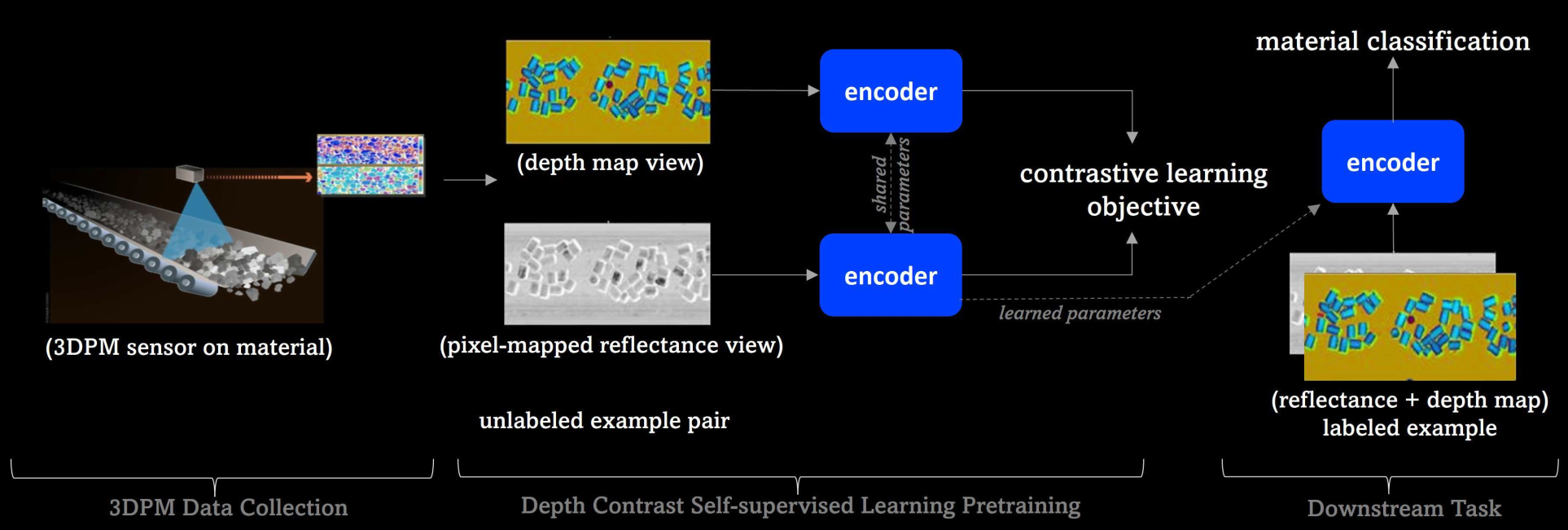
Our proposed method, Depth Contrast, utilizes these domain-specific insights to create a robust domain-aware self-supervised learning framework. By leveraging depth maps and reflectance images, this method transforms unlabeled data into a powerful learning signal, significantly enhancing material classification performance without the need for manual labeling.
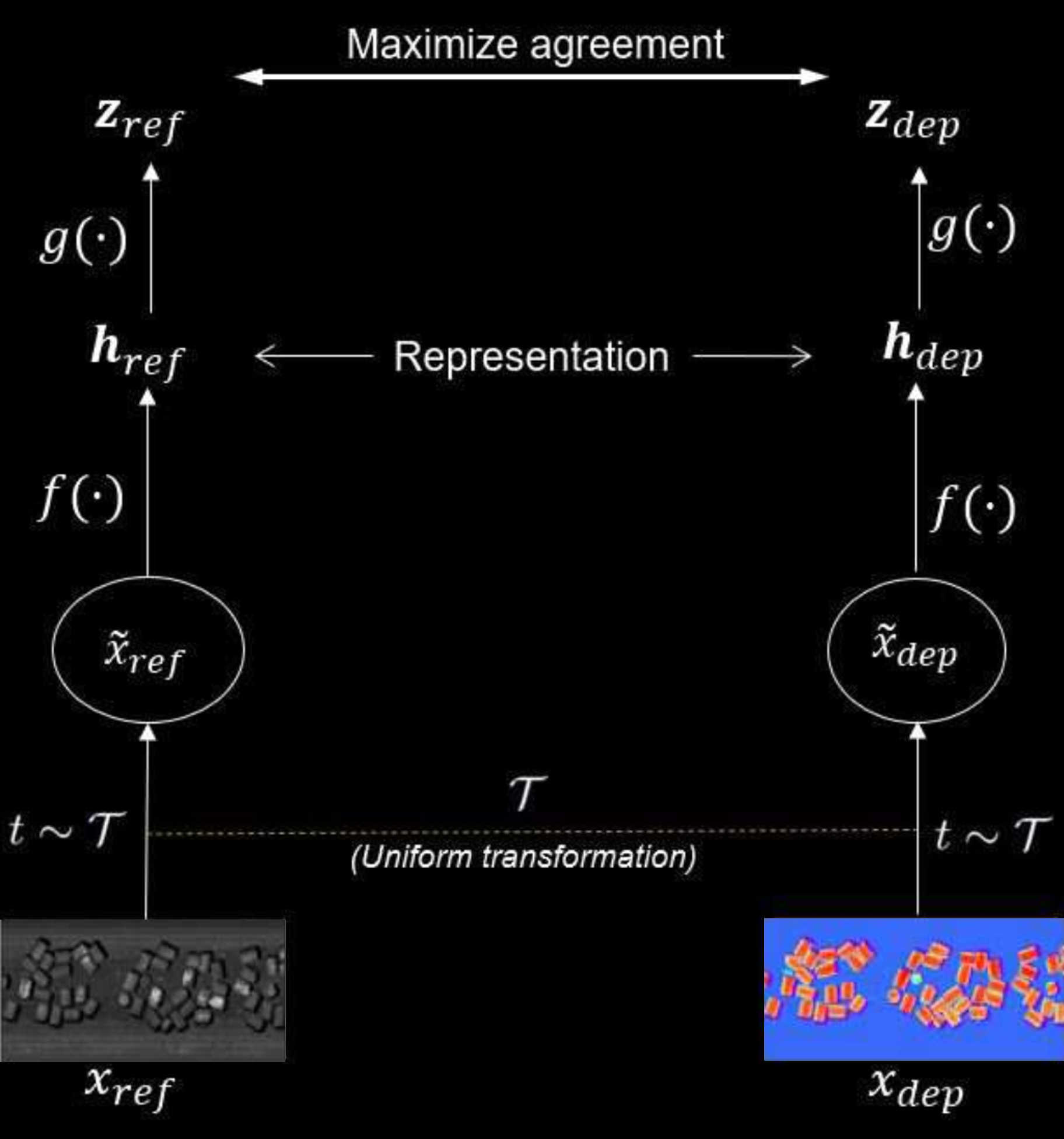
Depth Contrast employs contrastive learning techniques, where the model learns to maximize the similarity between augmented views of the same material while distinguishing it from different materials. This approach utilizes both reflectance and depth map images, creating representations that are more robust to the variations in material properties.
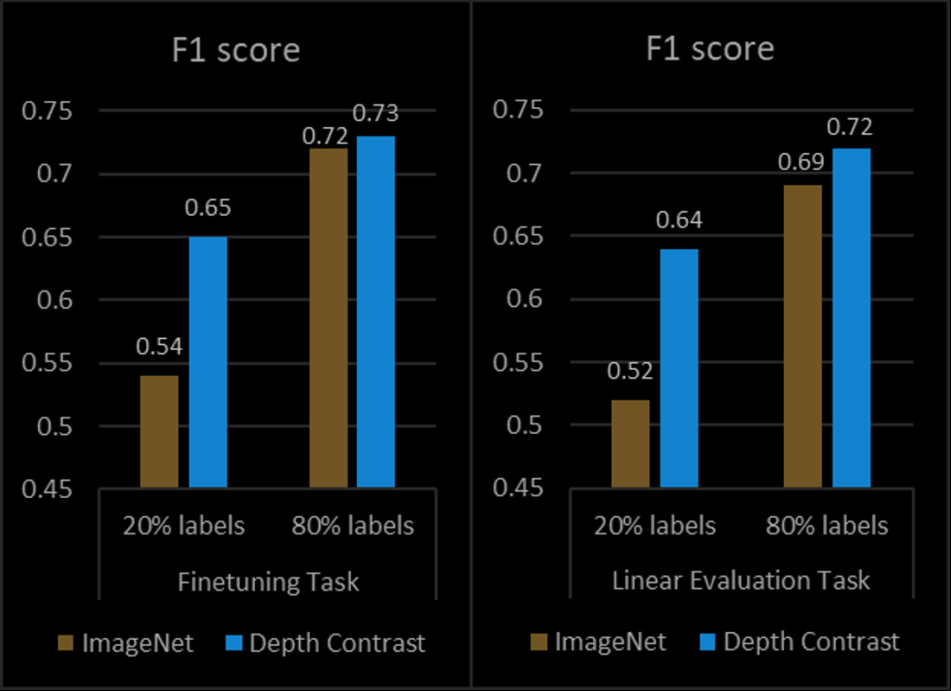
Key Outcomes:
- Improved Performance: Depth Contrast achieves an F1 score of 0.73 in fully supervised settings, outperforming traditional ImageNet transfer learning methods.
- Label Efficiency: In semi-supervised settings, Depth Contrast shows an 11% improvement over ImageNet models when only 20% of labeled data is used.
- Generalization: The method demonstrates robust performance even when used as a feature extractor, highlighting its generalization capabilities.
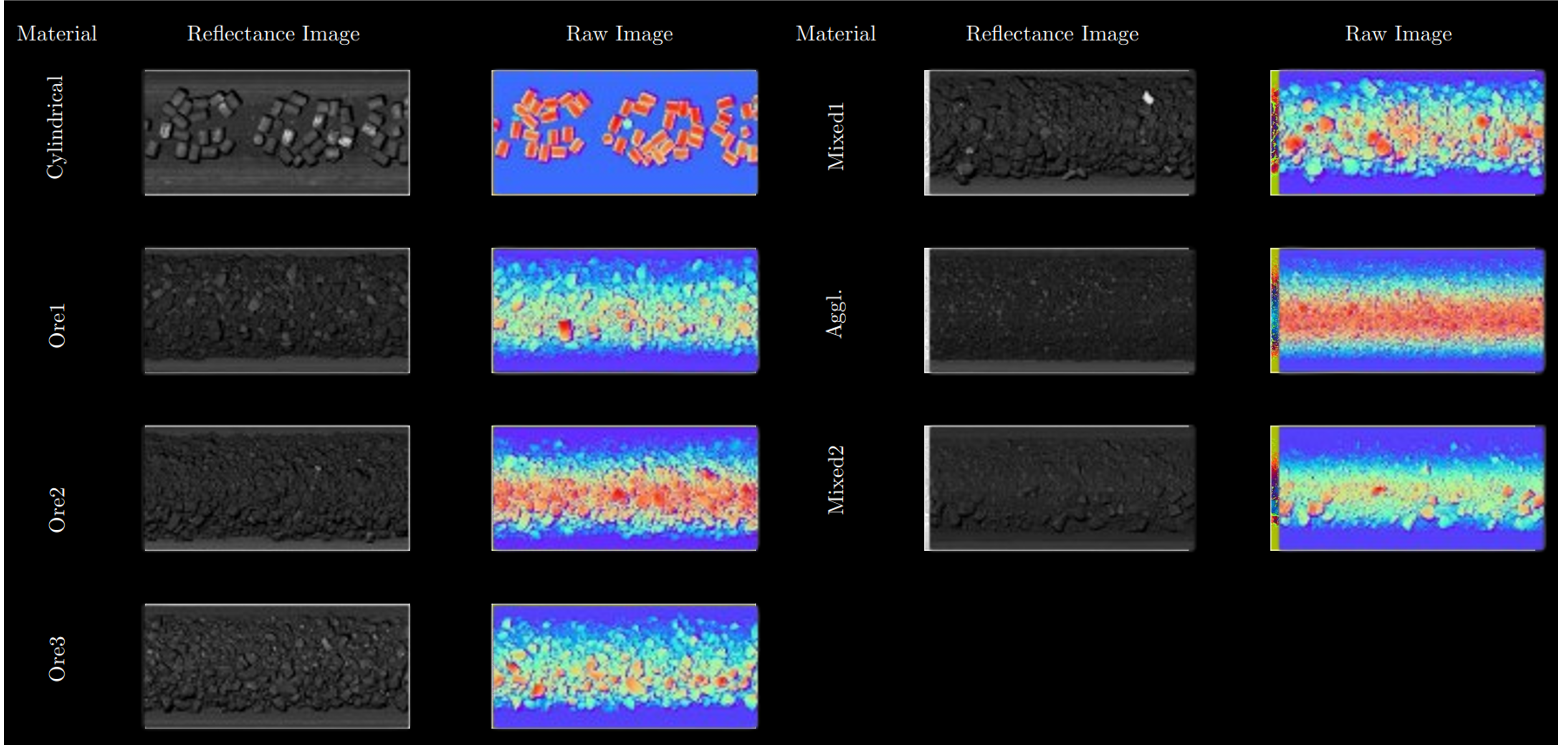
Ablation Study: Detailed experiments revealed that the combination of depth and reflectance images provides the best representation, with consistent performance improvements across various architectures and data conditions.
This domain-aware, self-supervised approach leverages the unique properties of depth and reflectance data from the 3DPM sensor to enhance material classification tasks, setting a new benchmark in the mining industry.
Read Paper @ arxiv Read Paper @ Springer Source Code @ Github Check poster
Chhipa, P.C. et al. (2023). Depth Contrast: Self-supervised Pretraining on 3DPM Images for Mining Material Classification. In: Karlinsky, L., Michaeli, T., Nishino, K. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022 Workshops. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13807. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25082-8_14