Open Vocabulary Object Detectors- Robustness Challenges under Distribution Shifts
European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops 2024
Read Paper Source Code @ Github Check poster Watch Video @ Youtube
VLM-based open-vocabulary object detectors extends the capabilities of traditional object detection frameworks, enabling the recognition and classification of objects beyond predefined categories. Investigating OOD robustness in recent open-vocabulary object detection is essential to increase the trustworthiness of these models. This study evaluates the zero-shot robustness of three cutting-edge open-vocabulary object detection models—OWL-ViT, YOLO World, and Grounding DINO. We tested their performance across distribution shifts using the COCO-O, COCO-DC, and COCO-C benchmarks. Our experiments reveal challenges related to information loss, corruption, adversarial attacks, and geometrical deformations, driving the ongoing pursuit of improved model robustness in real-world scenarios.
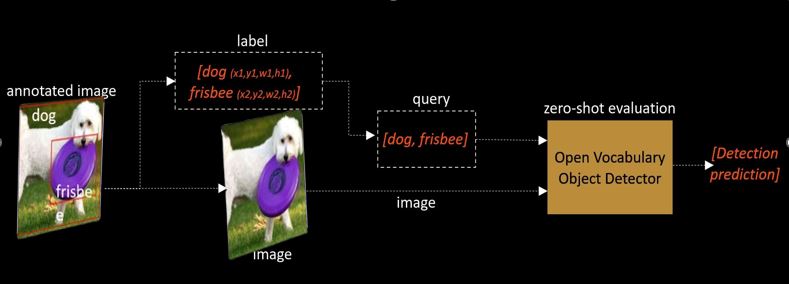
This study choses three prominant and recent open-vocabulary object detectiomn models to do comparative analysis.
- OWL-ViT ECCV 2022 - Builds on the Vision Transformer (ViT) by integrating text embeddings for open-vocabulary detection. It removes the final token pooling layer, adds lightweight classification and box prediction heads, and fine-tunes on image-text data. This enables zero-shot detection across diverse categories with high accuracy.
- YOLO-World CVPR 2024 - Enhances the YOLO model with real-time open-vocabulary detection using the RepVL-PAN and region-text contrastive loss. It achieves strong visual-semantic alignment and maintains efficiency, making it effective for detecting a wide range of objects in a zero-shot manner.
- Grounding DINO ECCV 2024 - Combines the DINO transformer with grounded pre-training to fuse language and vision for arbitrary object detection. It excels at language-guided detection and understanding objects from category names or referring expressions, making it versatile for both open-vocabulary detection and referring expression comprehension.
OVOD models were exposed to three public out-of-ditribution benchmarks which are dedicatly built for introducing distribution shifts from varius factors.
- COCO-O - A dataset testing object detection under natural distribution shifts like occlusion, blurring, pose variation, and illumination differences. It contains 6,782 images across six subsets: weather, painting, handmade, cartoon, tattoo, and sketch.
- COCO-DC - Focuses on object detection robustness with 1,127 images separated from their backgrounds. It features four subsets: Adversarial, BLIP-2 Caption, Color, and Texture to test models under diverse background conditions.
- COCO-C - Introduces 15 image corruption types (e.g., noise, blur, weather) with five severity levels, assessing model performance under unseen distortions across various challenges.
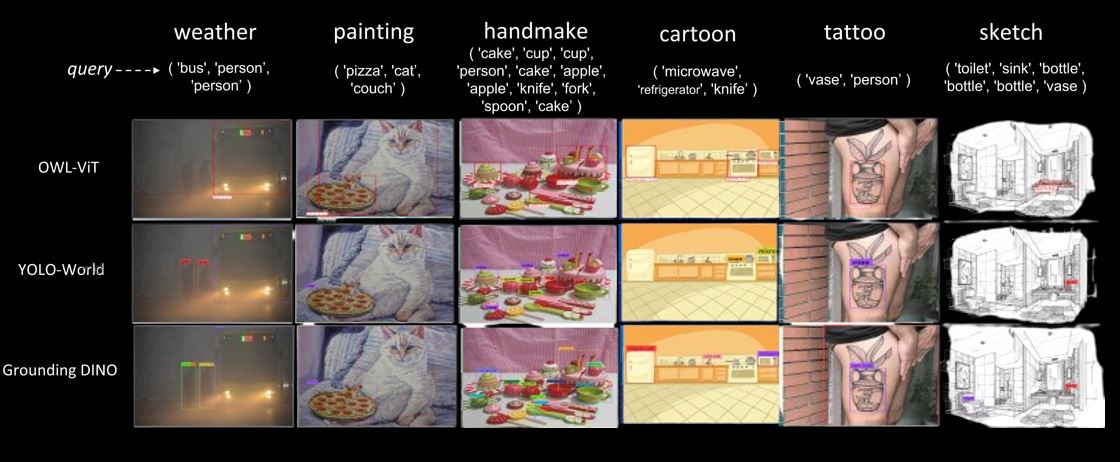
The notable observation suggests that all three open-vocabulary foundation model-based object detectors, when subjected to degradation of image quality and distribution shift, exhibit significant deviations in performance. This indicates an inherent relationship between OV object detectors and the quality of data.
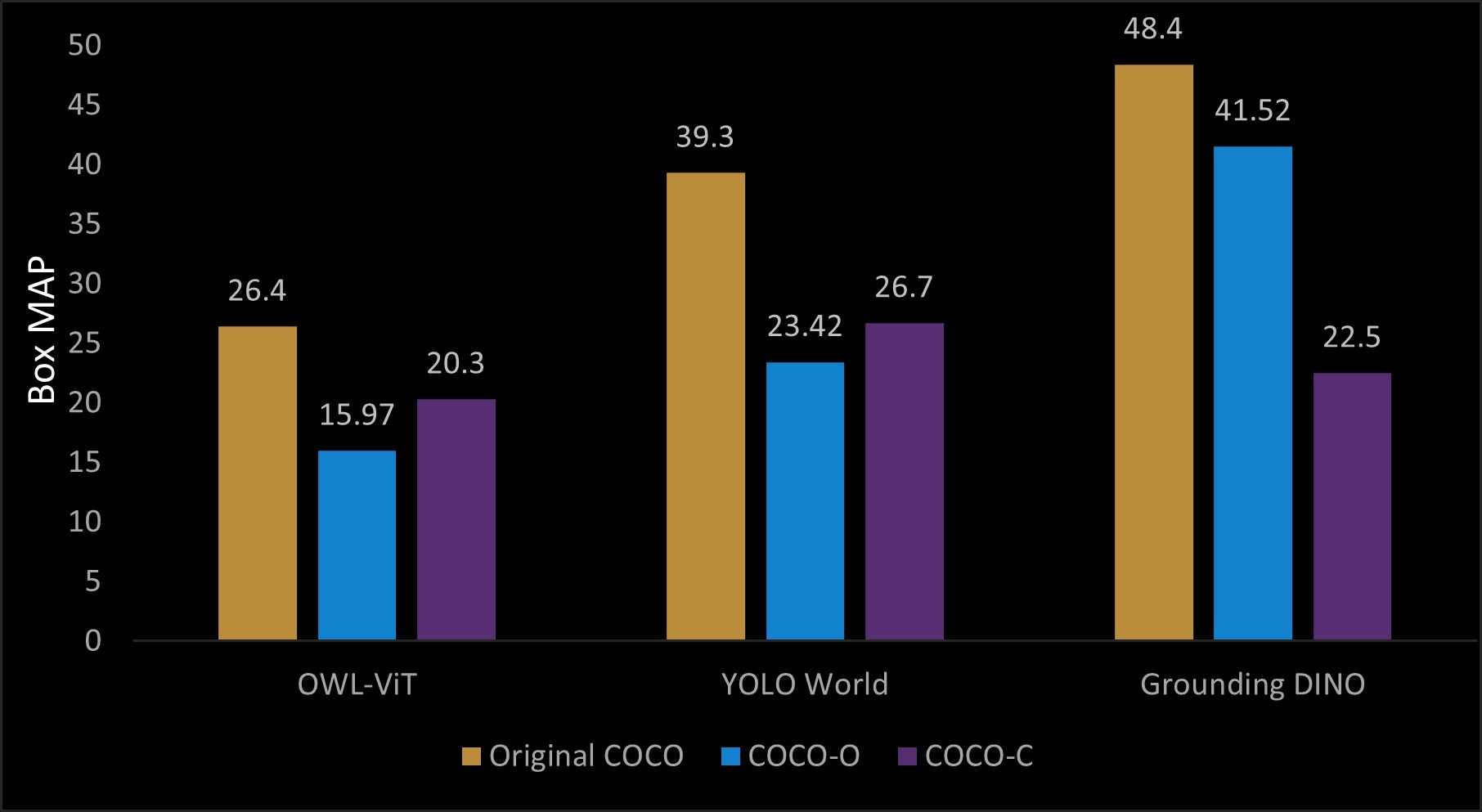
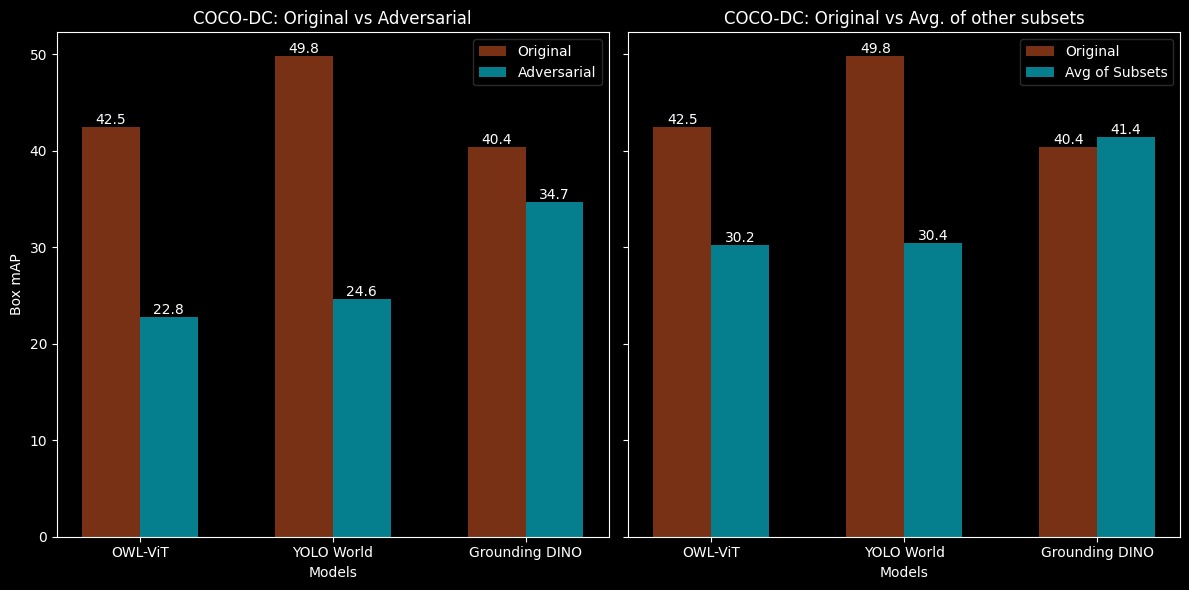
We explore one of the first approaches to evaluate zero-shot open-vocabulary foundation models from a robustness perspective under distribution shifts. By analyzing three recent object detection models across public benchmarks, we highlight the significant challenges posed by out-of-distribution shifts, which cause performance drops. Our findings suggest the need for further research into this area. Combining vision-language models with effective prompt engineering may pave the way for more robust open-vocabulary detectors, ultimately improving their reliability and enabling broader applications across various fields. Please read the paper for detailed analysis and inisghts.
Read Paper Source Code @ Github Check poster Watch Video @ Youtube
Chhipa, Prakash Chandra, et al. “Investigating Robustness of Open-Vocabulary Foundation Object Detectors under Distribution Shifts.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.14874 (2024).