Can Self-supervised Representation Learning Methods Withstand Distribution Shifts and Corruptions?
International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops 2023
Read Paper Source Code @ Github Check poster Download Pretrained Models Download ImageNet-PD
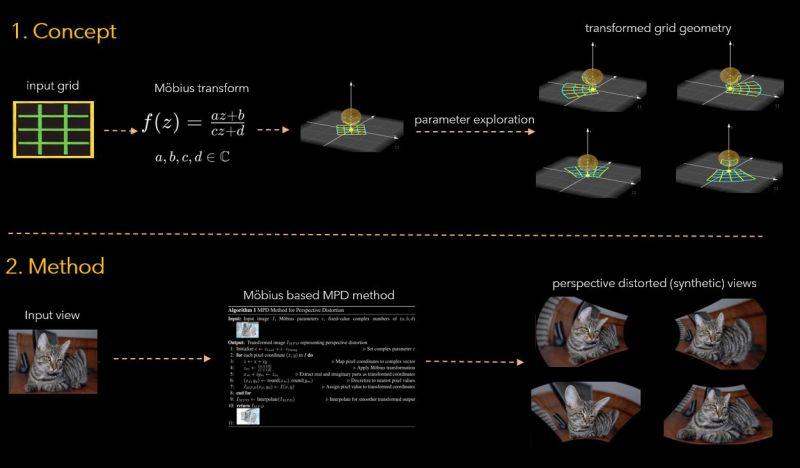
Perspective distortion significantly alters the appearance of objects in images. It can change their shape, size, orientation, angles, and the spatial relationships between them in ways that might not be expected.
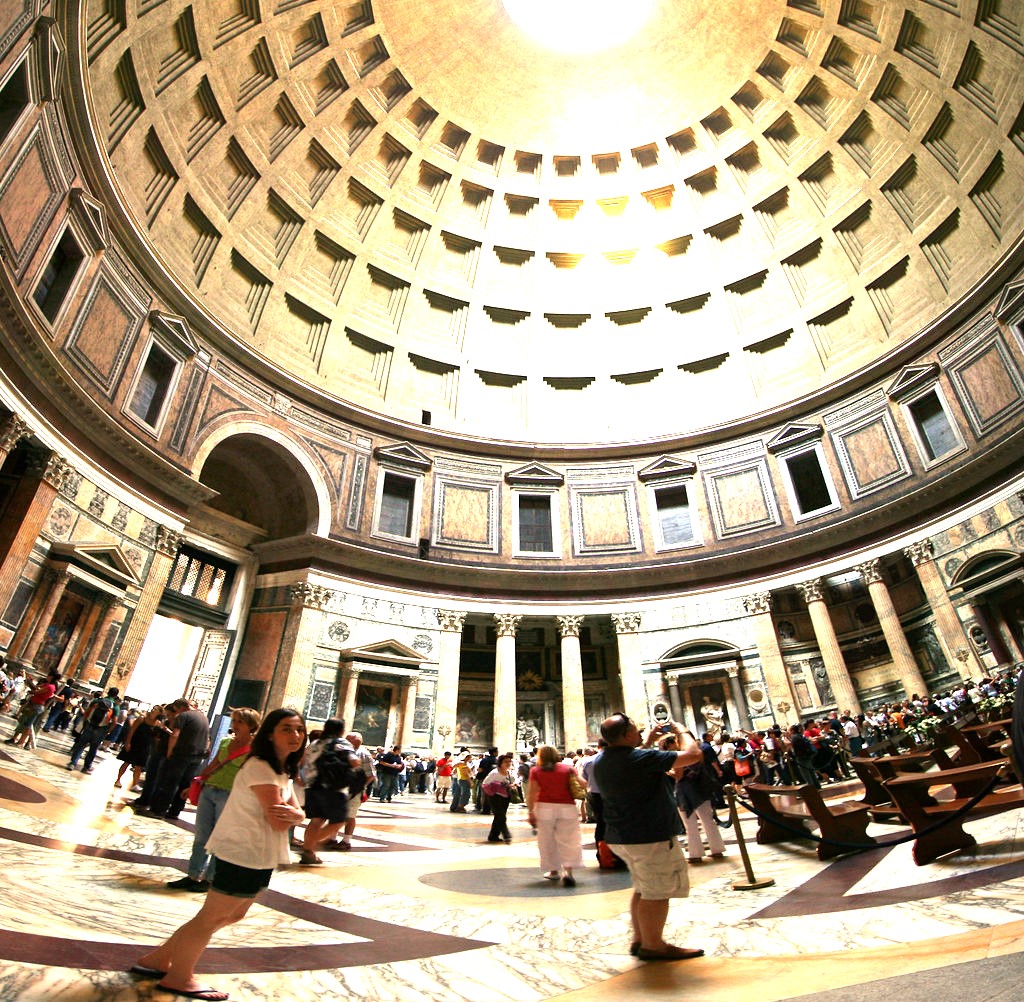
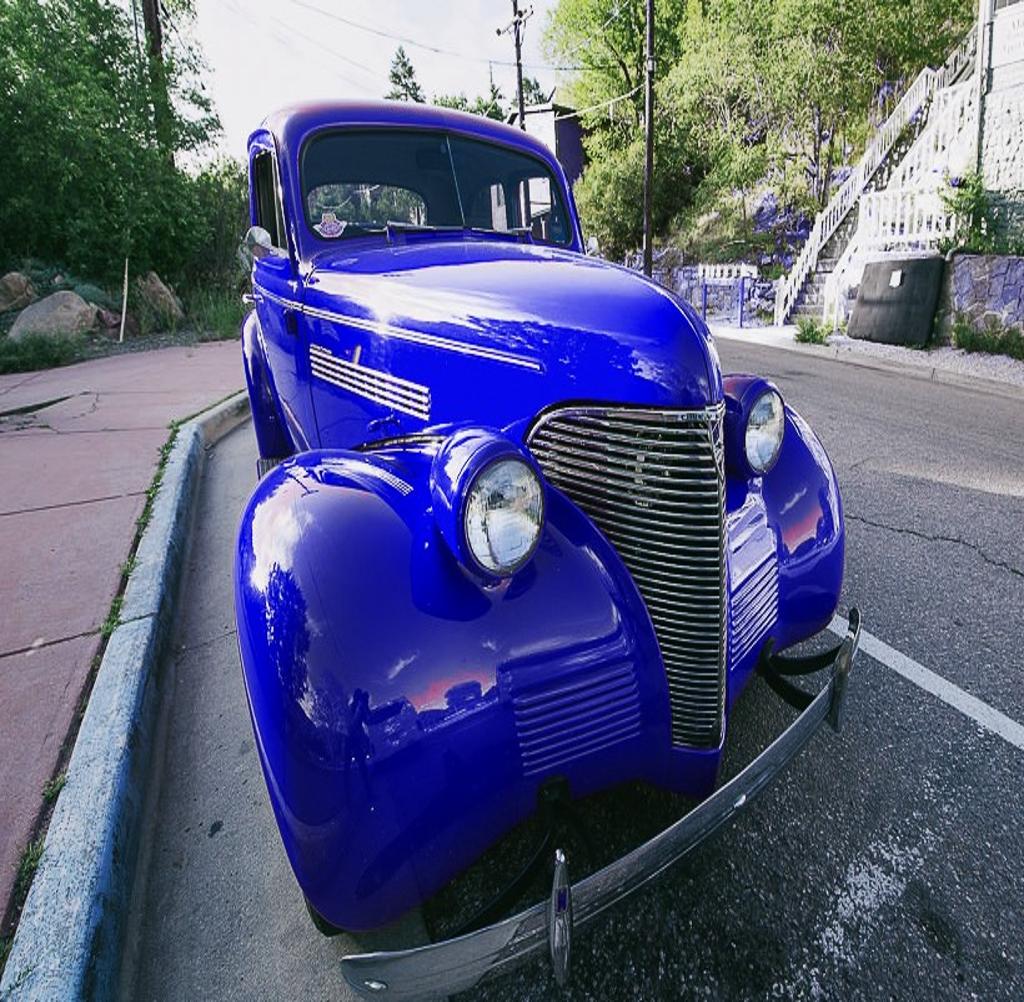
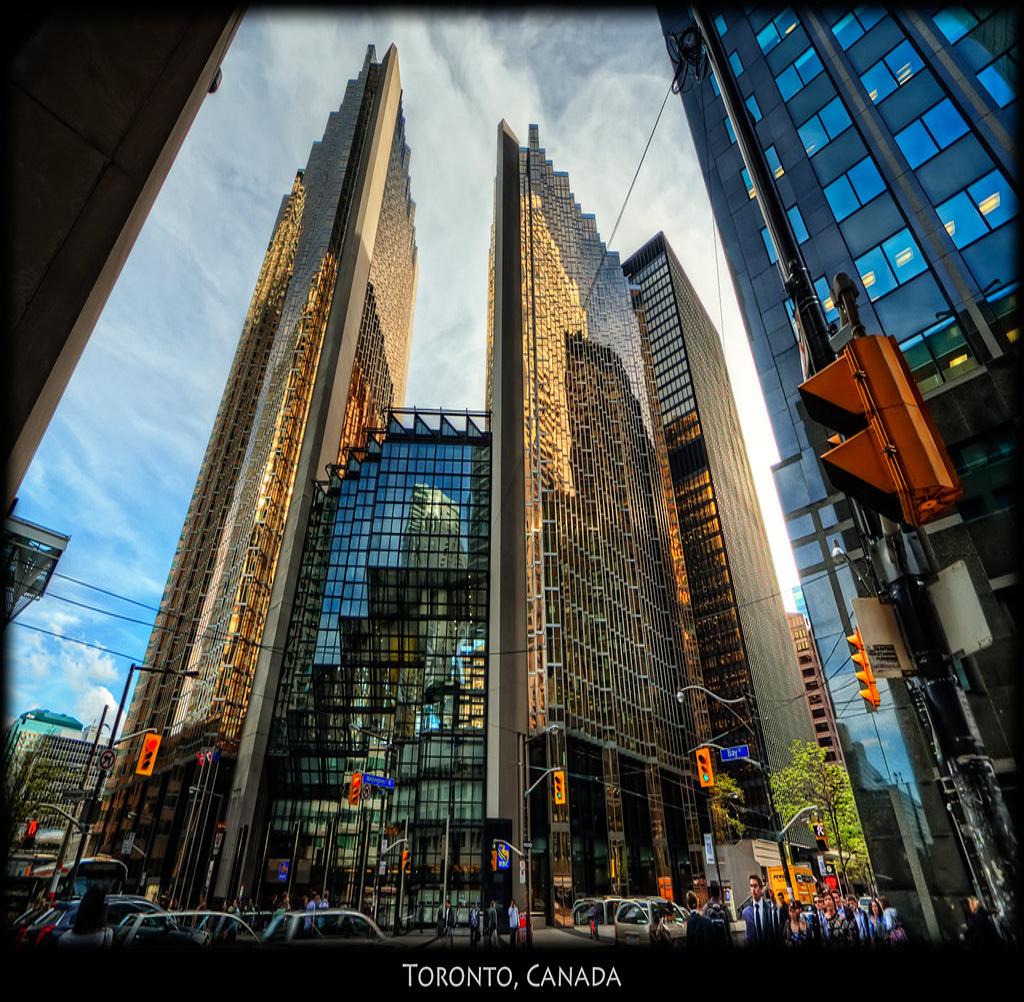



How perspective distortion alters the appearance? When same object captured from different viewpoints due to different location of camera, it captures the shape of image differently and distortion takes places naturally. Look at the visual here. Changes in shape of the object, changes the underlying distrutions. There are many such parameters like camera location has role in it.
What are the challenges?
- Data on which vison models are trained do not have exposure to intented perspectively distorted examples so no robustness against unprecedent perspective disrotion.
- Estimating camera’s intrinsic and extrinsic parameters are challenging and doing it precisely is next to impossible so it prevents synthesizing perspective distortion
- Distortion correction methods makes computer vision tasks a multi-step approach, first correction then vision task learning so its not efficient for real-world applications
Proposed methodology- This work focus on mittigating perspective distortion by exposing vision models to perspectively distorted examples. These examples are neither created using camera parameters nor naturally collected but synthesized by mathematically modelling the perspective distortion.
How MPD works? This work shares mitigating perspective distortion (MPD) method by first underatanding the non-linear nature of perspective distortion then employing a fine-grained parameter control on a specific family of Möbius transform to model real-world distortion without estimating camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters and without the need for actual distorted data. MPD leaverages Möbius’s conformal and non-linear nature in complex space. MPD takes images to complex space, transform, and then get it back to pixel space.
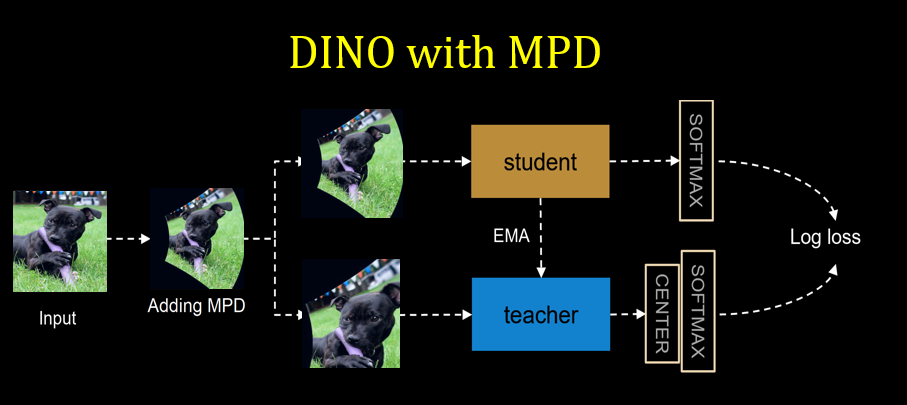
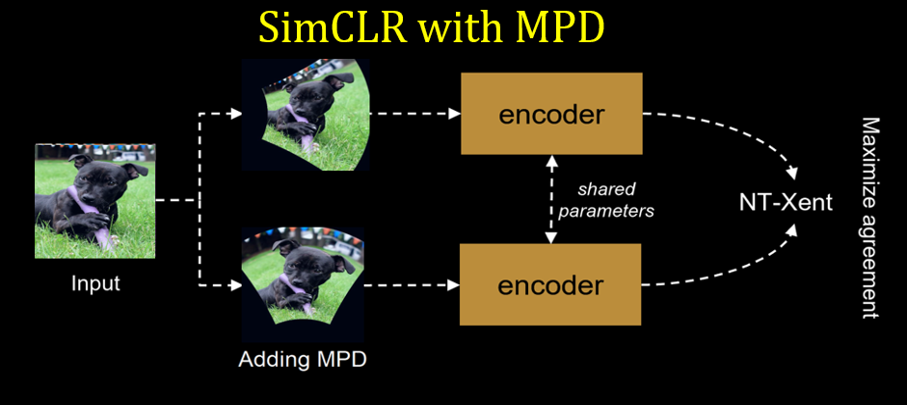
Integrating MPD- MPD gets easily integrated as augmentation method into learning pipline, be it supervsied training or self-supervised pretraining. In this work MPD explored with two self-supervsied methods SimCLR and DINO.
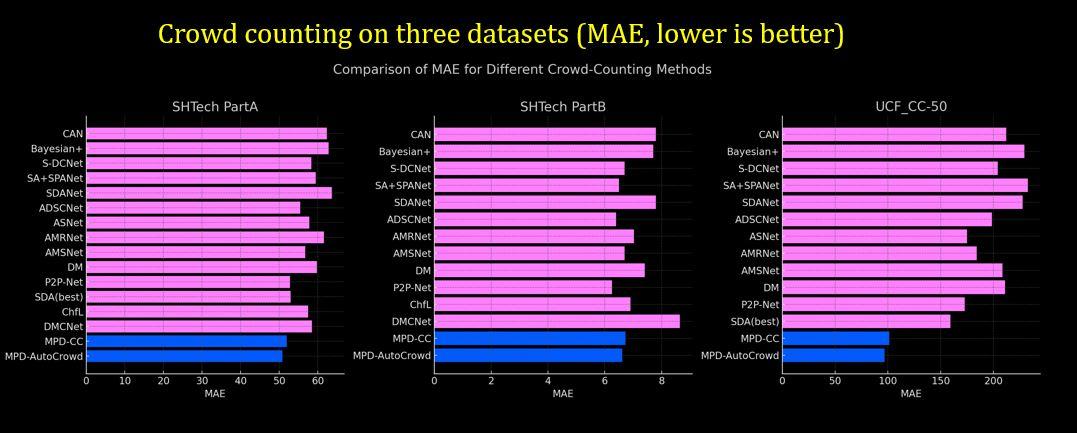
When it comes to adapting MPD to other real-world applications, MPD gets adapted easily with multiple computer vision applications including crowd counting, person re-identificaiton, fisheye view, and object detection.
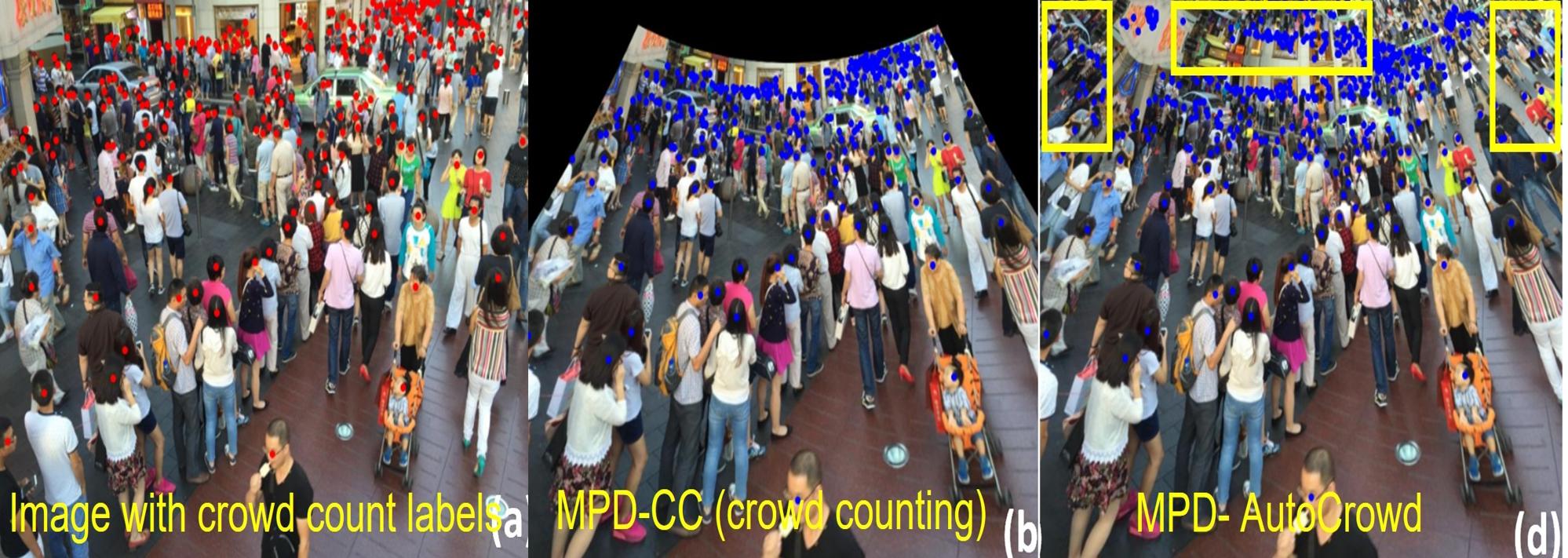
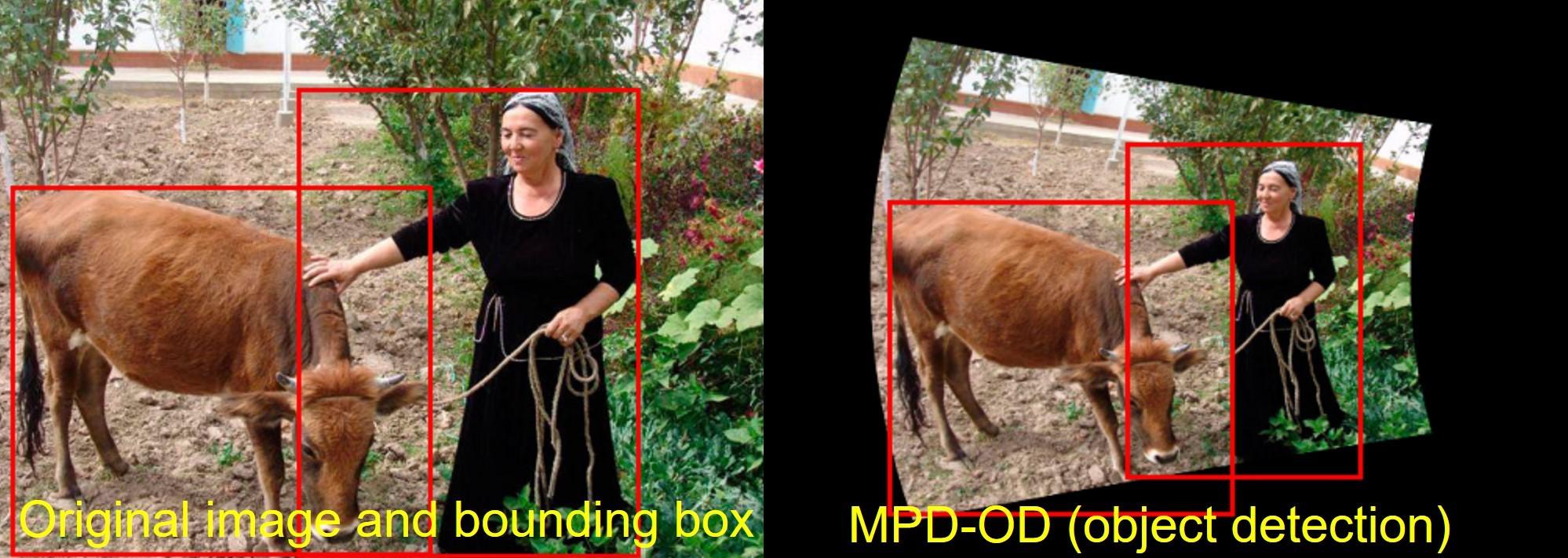


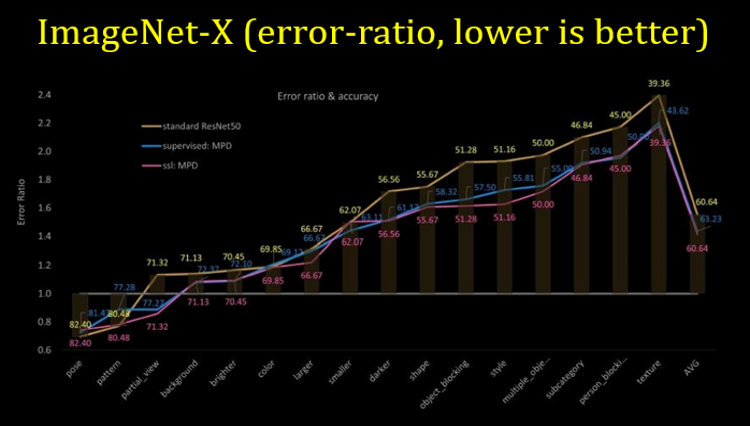
MPD offers robustness- The proposed method MPD outperforms on existing perspective distortion affected benchmarks, ImageNet-E and ImageNet-X. MPD significantly improves performance on ImageNet-PD (check it down) while consistently performing on standard data distribution. MPD improves performance on three PD-affected real-world applications: crowd counting, fisheye image recognition, and person re-identification and one PD-affected challenging CV task: object detection.
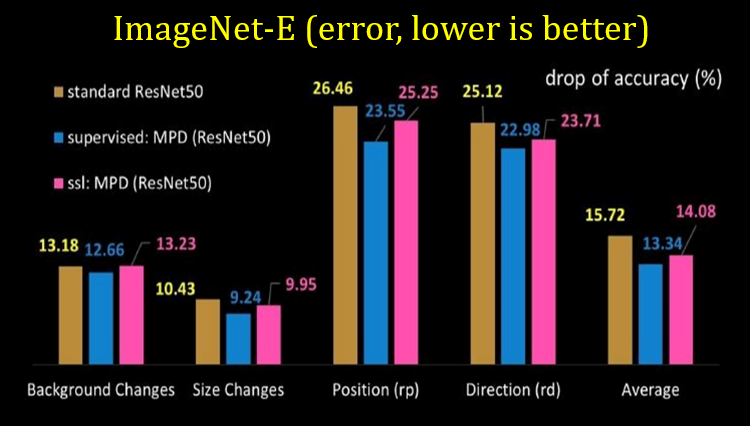
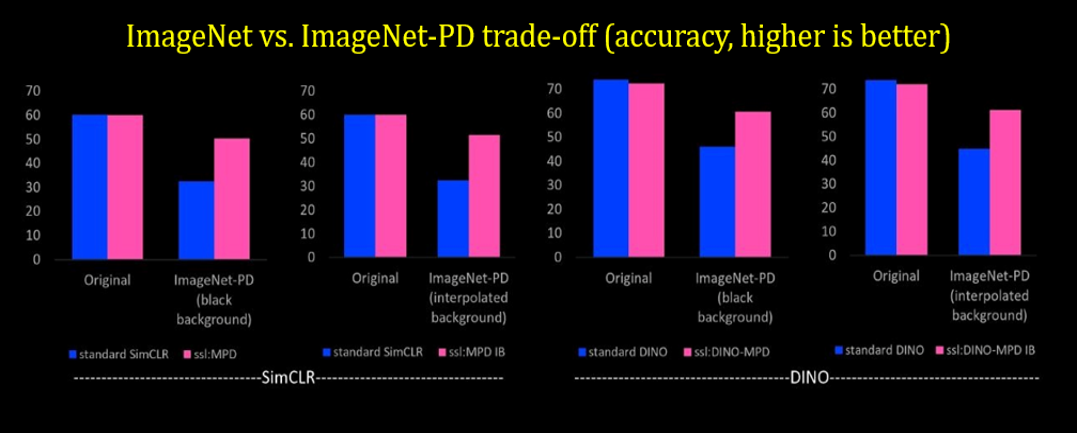
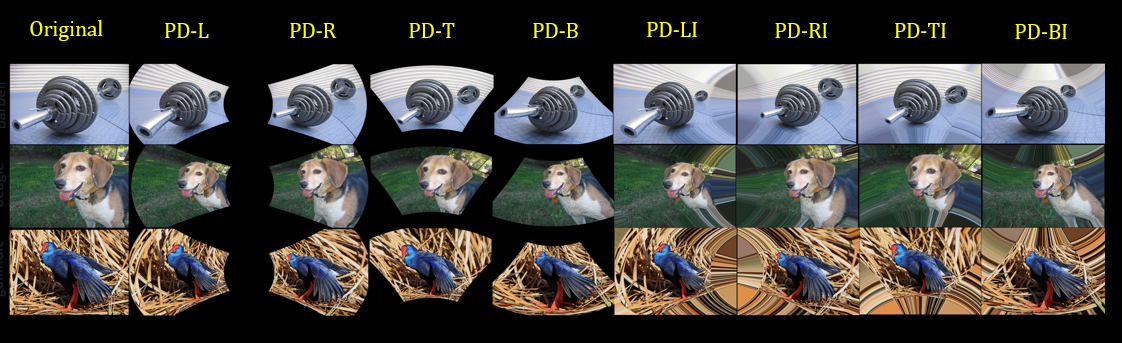
A dedicated perspectively distorted benchmark dataset This work shares a new benchmark ImageNet-PD to evaluate the robustness of computer vision models against perspective distortion and address the non-availability of a suitable benchmark. ImageNet-PD derived from the original ImageNet\cite validation set, has eight subsets, four corresponding to four orientations (left, right, top, bottom) with black background and other four subsets with the same orientations but with integrated padding background.
Read Paper Source Code @ Github Download Pretrained Models Download ImageNet-PD
Prakash Chandra Chhipa, Johan Rodahl Holmgren, Kanjar De, Rajkumar Saini, Marcus Liwicki; Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, 2023, pp. 4467-4476